Nowadays, servers typically house all digital data that requires storage and say What Is A Cloud Database? Traditionally, it is hard to comprehend the number of servers needed for storing all the data. Humans may have to leave Earth because servers are taking over the entire planet.
The servers’ expense and upkeep are crucial, resulting in a significant need for substantial funds. Nonetheless, the rise of Cloud Database Systems offered a solution to conserve space and reduce costs associated with acquiring and upkeeping physical storage systems.
What Is A Cloud Database?

An Organization utilizes it to efficiently store, manage, and regulate data in a community or hybrid cloud environment. Accordingly, it may be offered as a managed database-as-a-service (DBaaS), deployed on a cloud-based virtual machine (VM), and managed by an internal IT team. Gain knowledge in Cloud Database for a promising career with lucrative pay.
How do Cloud databases work?
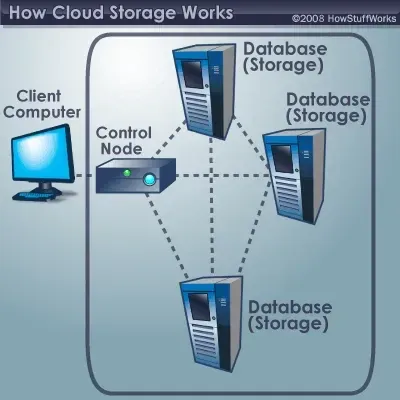
Moreover, businesses use databases for gathering, arranging, and providing data to employees and managers for operational and analytical purposes. Generally, Cloud databases typically offer equivalent data processing, management, and access functionalities as traditional on-premises databases. Normally, on-premises databases can be moved to the cloud, along with the applications they serve.
Factors Of A Cloud Database
The database holds significant importance within any IT setting. These are a few features and concerns that organizations should consider when assessing cloud databases for upcoming deployments.
- Execution of a task: When dealing with any IT system, it is crucial to prioritize this factor, especially when the database needs to handle demanding workloads. Scalability plays a role in ensuring that real-time processing jobs do not slow down. Another important factor to consider is the ability to monitor and optimize performance.
- Expense: Identically, the main cloud providers provide cost calculators online for free. These can be used to analyze various pricing models, service setups, processing regions, and other factors to manage resource needs and budgets.
- Availability: Obviously, It is important to assess the cloud provider’s uptime SLA, disaster recovery capabilities, data backup procedures, and high availability features.
Types Of Cloud Database
There may be a distinction between relational and non-relational databases in both the cloud and on-premise databases.
1. Relational Database
Moreover, users can enhance their comprehension of logical relationships by collecting information through pre-defined interactions using tables containing columns and rows in databases. Typically, they possess a set data representation and can be accessed and controlled using predetermined query language (SQL). Although, these databases manage large quantities of organized data with great reliability, durability, and efficiency.
2. Non-relational databases
It can store and handle various types of data such as email and mobile message text, documents, surveys, rich media files, and sensor data in an active manner. Besides, In separate relational databases, unstructured data is not tied to a particular format, allowing for storage and organization in any arrangement.
Operational Models
There are two operation models available such as Self-managed and Service database.
1. Self Managed
A traditional Self-Managed system is a Cloud Database housed on a virtual machine and is actively managed and operated by the organization. Once more, the user’s internal IT team is responsible for upkeeping and overseeing the database within this module format, with the user retaining greater authority.
2. Service Database
Accordingly, the second type is Database as a Service. Additionally, this service restores the database. The Cloud service provider’s physical infrastructure hosts it, with the provider taking responsibility for operational, maintenance, and administration database management duties. Moreover, this involves automatic setting up, cleaning, protecting, upgrading, and overseeing the health of the Cloud Database.
Characteristics Of Cloud Database
Here we can discuss some of the characteristics of a Cloud Database
- Resources Pooling
- On-Demand Self-Service
- Easy Maintenance
- Scalability And Rapid Elasticity
- Economical
- Measured And Reporting Service
- Security
- Automation
Advantages Of Cloud Database
- It Offers Flexibility– Besides, You can easily enter various technologies. This assists in speeding up innovation and constructing almost anything you can dream of. You have rights to resources like storage, computing, databases, data leaks, analytics, and machine learning as and when required. You can access technology services quickly and go from concept to execution more rapidly.
- Deploys Globally– Cloud Database quickly deploys globally to new geographic regions in just minutes. Furthermore, placing applications closer to end users can decrease latency and enhance their experience.
- Cost Optimization– Comparatively, the purchasing of hardware and software is eliminated by the Cloud Database. Moreover, the expenses associated with establishing and operating physical data centers on location are also eradicated. Additionally, this avoids the cost associated with server racks, constant electricity usage for power and cooling, and the need for IT professionals to oversee the infrastructure. Finally, this aids in rapidly optimizing the costs related to IT.
- Boosts Efficiency-Further, Setting up and maintaining hardware, software updates, and other tasks are eliminated with Cloud Database, leading to enhanced productivity. This aids IT teams in dedicating additional time to reaching crucial business objectives, consequently increasing their productivity.
Disadvantages Of Cloud Database
- Cloud Security And Data Protection: Simultaneously, storing data and important business files in virtual data centers poses numerous risks. Therefore, Some potential risks include data loss or theft, data leakage, account or service hijacking, insecure interfaces and APIs, technological vulnerabilities in shared environments, and denial of service attacks.
- Limited Control:- The cloud service providers own, manage, and monitor the cloud infrastructure. The control the customer has is minimal. The client cannot do main administrative duties like changing firmware, managing servers, or accessing server shells.
- Cloud Downtime: This can occur due to technical issues like reboots, network outages, and periods of inactivity. These incidents have the potential to harm companies. They can disrupt business operations and processes.
- Exposure To Attacks: In a Cloud Database, all components being online increases susceptibility to potential vulnerabilities. Occasionally, you may experience intense breaches and attacks on your security.
Conclusion
Additionally, Cloud Databases cut down on business infrastructure and expenses by removing the requirement for on-premise servers and upkeep. Moreover, in simpler terms, its management serves as an efficient way to store data and files. It offers suitability, uniformity, and protection. Additionally, users can retrieve their data from any location without data loss if their computer, mobile device, or other electronic device is compromised.
Ans. Cloud databases are responsible for handling and storing structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. Despite this, they provide many benefits of cloud computing, like rapidity, expandability, flexibility, and cost savings.
Ans. The Cloud Database is set to experience significant expansion in the future due to technological advancements, regulatory compliance, and the growing utilization of cloud computing in different sectors.
Ans. Many cloud providers have strong security measures such as physical security at data centers and advanced security for software and applications.
Ans. Affirmative! Google SQL is specifically a type of database. Google SQL offers a customized version of SQL Server, MySQL, and Postgre SQL for management purposes.
Ans. Moreover, Cloud cost management offers immediate visibility into cloud spending and cost information, guaranteeing that businesses are charged solely for the resources they utilize.



